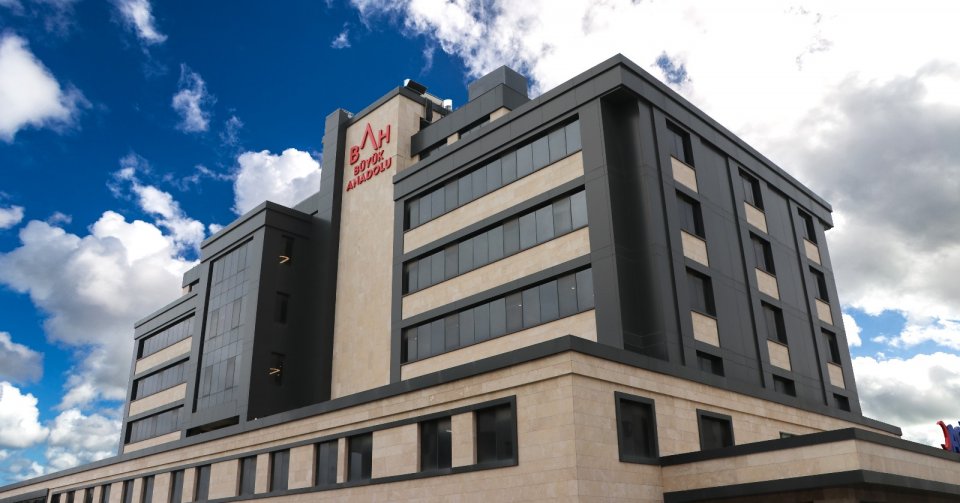
Improve Your Quality of Life with Exceptional Care
At Büyük Anadolu Hospital, our mission is to provide world-class medical care with compassion, respect, and a personal touch. Whether you are seeking advanced treatments or ongoing care, we are here to be your trusted healthcare partner.

30
150
1 M +
Treatments
WHY CHOOSE BUYUK ANADOLU HOSPITAL?
Since 1997, Büyük Anadolu Hospital has been a trusted leader in delivering world-class healthcare in Türkiye, combining advanced medical technology with compassionate, patient-focused care. With a team of over 100 internationally trained specialists, we offer innovative, evidence-based treatments and personalized care plans designed to ensure safe, effective, and long-lasting results. Our all-inclusive services — including comfortable accommodation, VIP transfers, translation assistance, and 24/7 medical support — provide a seamless experience from your first consultation to full recovery. Having served thousands of patients from around the world for more than three decades, we continue to uphold our commitment to excellence, safety, and comfort, making us the preferred choice for international patients seeking high-quality medical treatment.

Transfer
We organize seamless airport and hospital transfers, ensuring you reach your treatment comfortably and on time.
Assurance
Before any procedure, we provide full consultation and clarity, so you feel confident and informed every step of the way.
Accommodation
Enjoy 5-star hotel stays and in-hospital accommodations & arranged for your convenience throughout your treatment journey.
Treatment
Our dedicated team supports you throughout the treatment, providing guidance & care at every stage.
Follow Up
We continue post-treatment support and follow-up, ensuring your recovery is smooth and any concerns are promptly addressed.
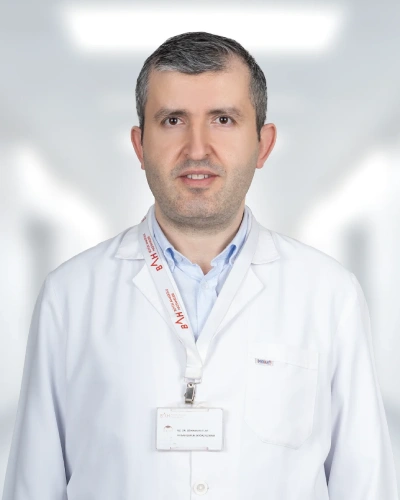
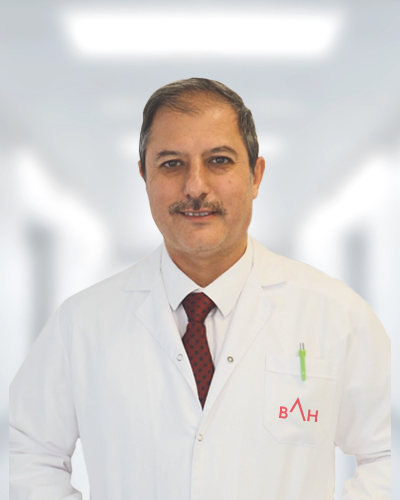
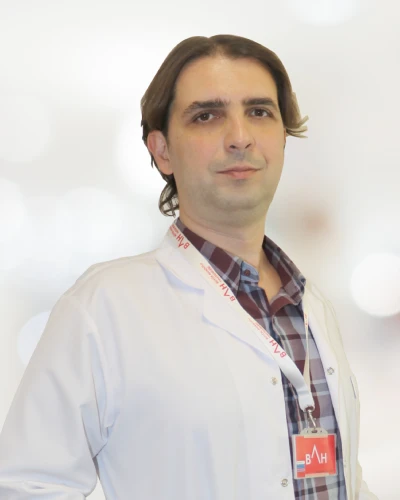
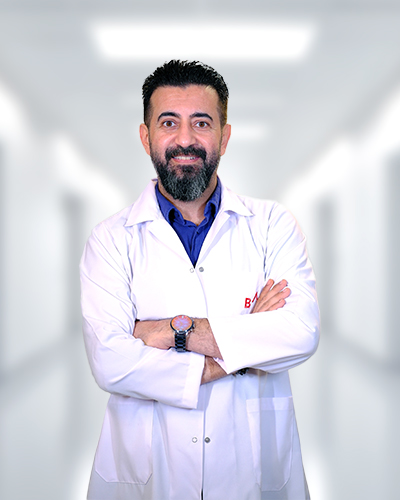
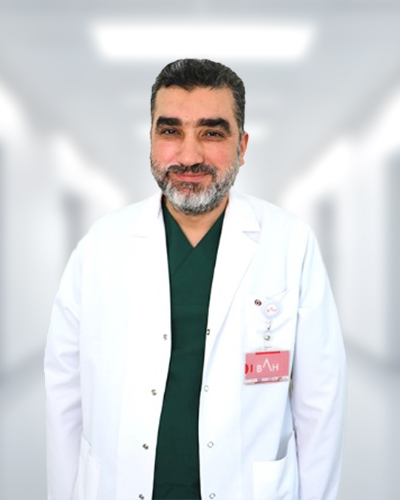
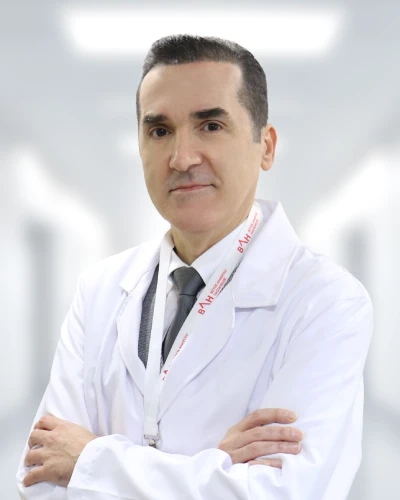
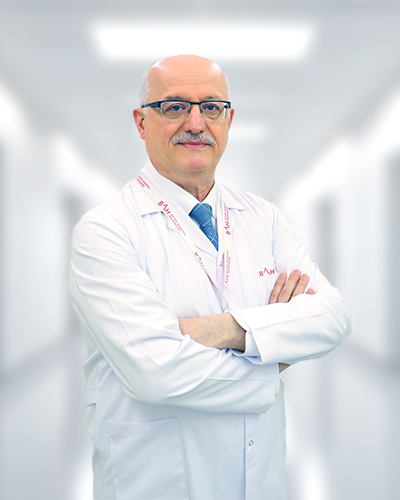
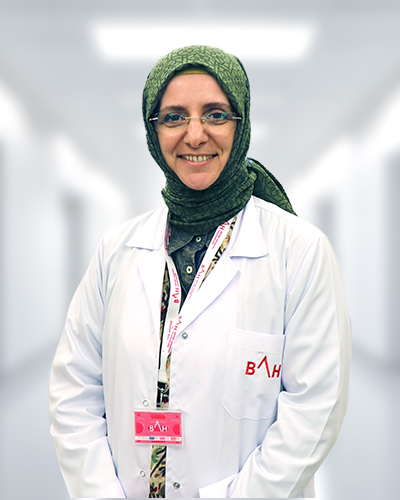
Meet Our Physicians
Free Preliminary Interview Form
Please feel free to contact our friendly patient coordinators with any general or medical enquiry.